43 coupon rate and ytm
Difference Between YTM and Coupon rates Nevertheless, the term 'coupon' is still used, even though the physical object is no longer implemented. Summary: 1. YTM is the rate of return estimated on a bond if it is held until the maturity date, while the coupon rate is the amount of interest paid per year, and is expressed as a percentage of the face value of the bond. 2. Bond Yield to Maturity (YTM) Calculator - DQYDJ We calculated the rate an investor would earn reinvesting every coupon payment at the current rate, then determining the present value of those cash flows. The summation looks like this: Price = Coupon Payment / ( 1 + rate) ^ 1 + Coupon Payment / ( 1 + rate) ^ 2 ... + Final Coupon Payment + Face Value / ( 1 + rate) ^ n
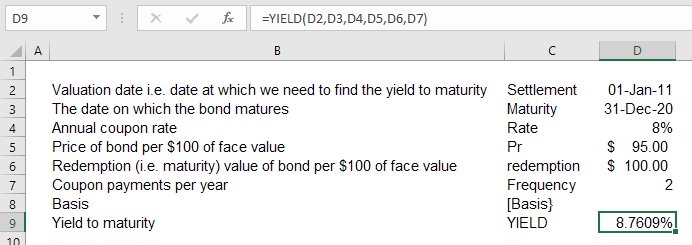
Yield to maturity formula - sqv.vogood.fr Current Yield Formula . To determine the current yield , you need to divide the amount of the coupon rate by the price the bond is currently selling for. For the coupon amount, you would need to know the cash value that you are earning from the bond because of its interest. So, you would divide the par value by its interest rate and use the. Yield to maturity (YTM) is an ...
Coupon rate and ytm
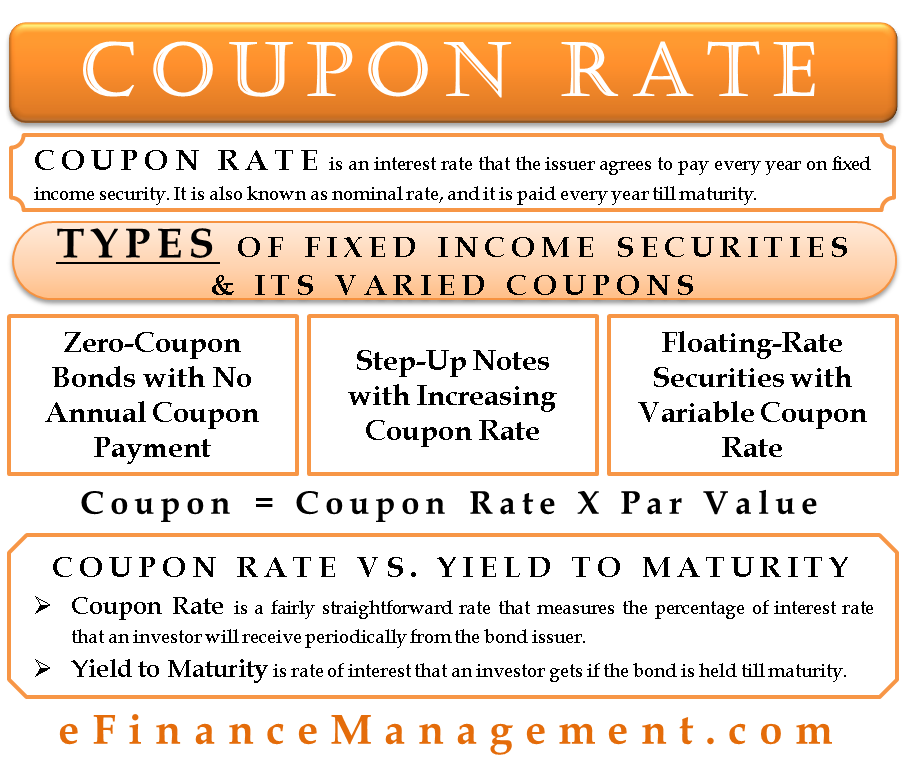
Coupon Rate Definition - Investopedia The coupon rate, or coupon payment, is the nominal yield the bond is stated to pay on its issue date. This yield changes as the value of the bond changes, thus giving the bond's yield to maturity... Yield to Maturity vs. Coupon Rate: What's the Difference? - Investopedia To calculate the bond's coupon rate, divide the total annual interest payments by the face value. In this case, the total annual interest payment equals $10 x 2 = $20. The annual coupon rate for... Yield to Maturity (YTM) - Definition, Formula, Calculation Examples Step by Step Calculation of Yield to Maturity (YTM) The steps to calculate Yield to Maturity are as follows. Gather information on the bond-like its face value, months remaining to mature, the bond's current market price, and the bond's coupon rate.
Coupon rate and ytm. Coupon vs Yield | Top 5 Differences (with Infographics) - WallStreetMojo The yield to maturity (YTM) refers to the rate of interest used to discount future cash flows. read more is $1150, then the yield on the bond will be 3.5%. Coupon vs. Yield Infographic Let's see the top differences between coupon vs. yield. Current Yield vs. Yield to Maturity: What's the Difference? A bond's yield is measured in different ways. Two common yields that investors look at are current yield and yield to maturity. Current yield is a snapshot of the bond's annual rate of return, while yield to maturity looks at the bond over its term from the date of purchase. 1. Difference Between Coupon Rate and Yield to Maturity The main difference between Coupon Rate and Yield to Maturity (YTM) is that Coupon Rate is the fixed sum of money that a person has to pay at face value. In contrast, Yield to Maturity (YTM) is the amount a person will retrieve after the maturation of their bonds. The Coupon Rate is said to be the same throughout the bond tenure year. Understanding Coupon Rate and Yield to Maturity of Bonds Let's see what happens to your bond when interest rates in the market move. When bonds are initially issued in the primary market, the Coupon Rate is based on current market rates, hence YTM is equal to the Coupon Rate. In the example bond above, when you bought the 3-year RTB issued at the primary market, your YTM and Coupon Rate is 2.375%.
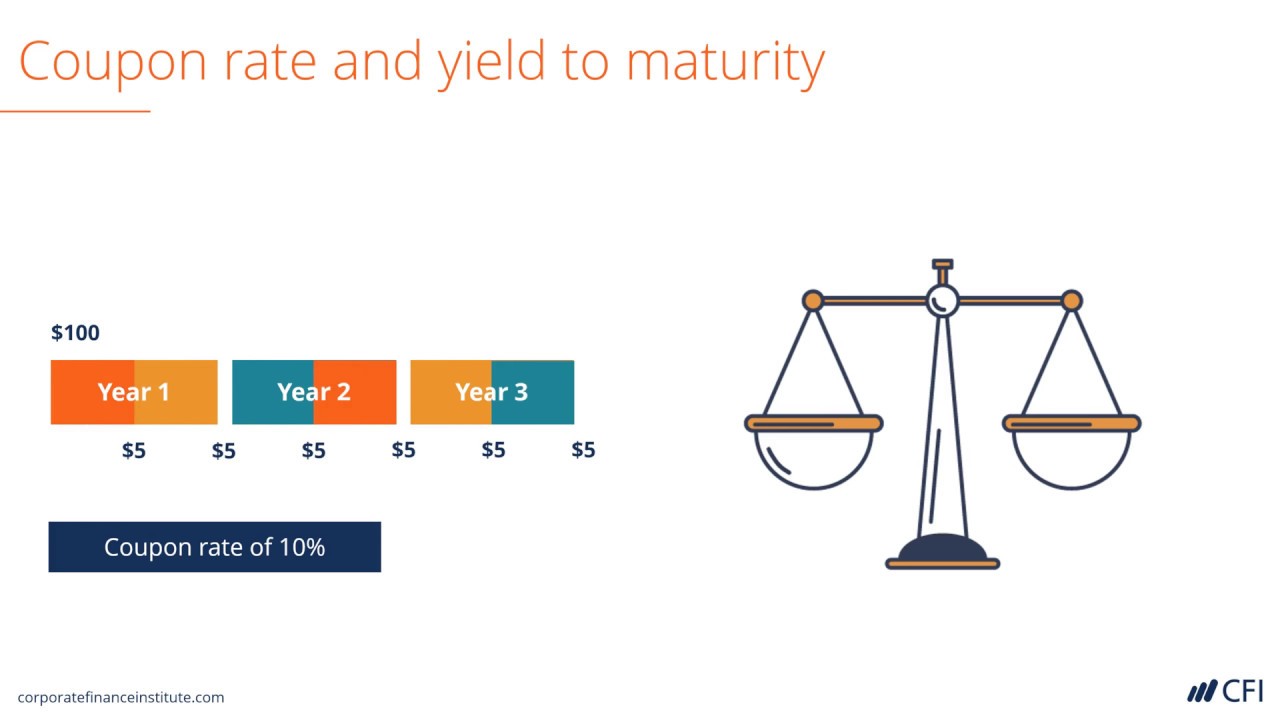
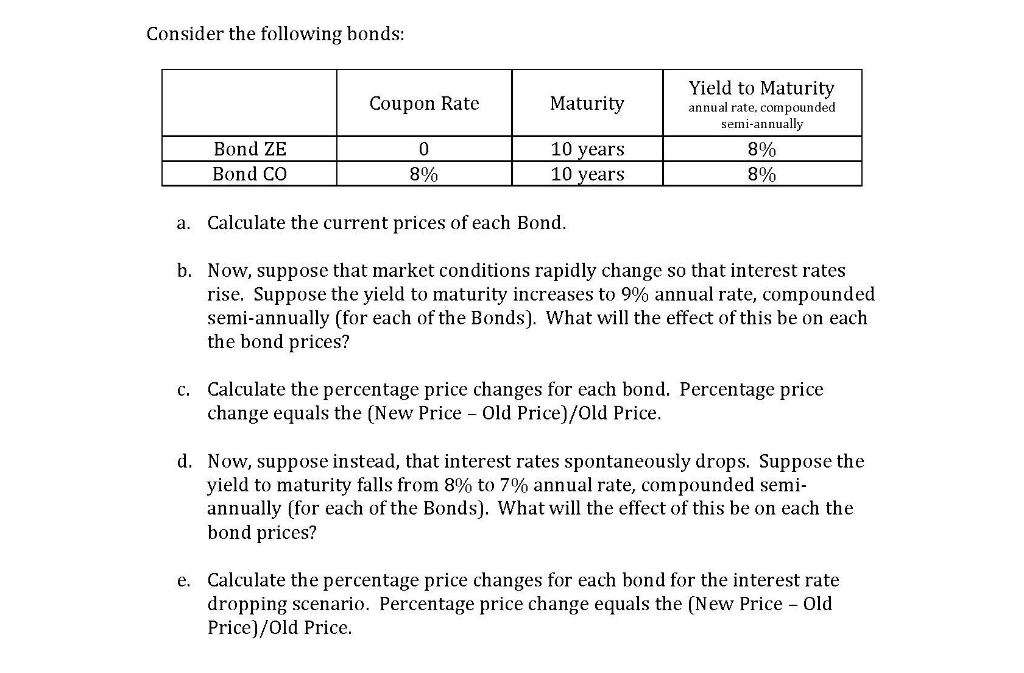
Difference between YTM and Coupon Rates A YTM, or yield-to-maturity, reflects the annual return an investor would receive if they held a bond until it matures. A coupon rate is the percentage of the face value of a bond that is paid out as interest to investors on a yearly basis. The higher the coupon rate, the more money investors will earn on their investment. Coupon Rate - Learn How Coupon Rate Affects Bond Pricing The coupon rate represents the actual amount of interest earned by the bondholder annually, while the yield-to-maturity is the estimated total rate of return of a bond, assuming that it is held until maturity. Most investors consider the yield-to-maturity a more important figure than the coupon rate when making investment decisions. Coupon Rate - Meaning, Calculation and Importance - Scripbox The main distinction between the coupon rate and YTM is the return estimation. The coupon rate payments are the same for the bond tenure. While the yield on maturity varies depending on various factors such as the number of years till maturity and the current trading price of the bond. Let's assume the couponrate for a bond is 15%. Calculating Cost of Debt: YTM and Debt-Rating Approach The YTM will be the rate at which the present value of all cash flows = $1,050. $$\$1,050 = \left ( \sum_ {t=1}^ {20} \frac {\$40} { (1+i)^ {t}} \right)+\frac {\$1000} { (1+i)^ {20}}$$ We can use a financial calculator to solve for i. In this case, i = 3.643%, which is the six-month yield. The annualized yield will be 7.286%.
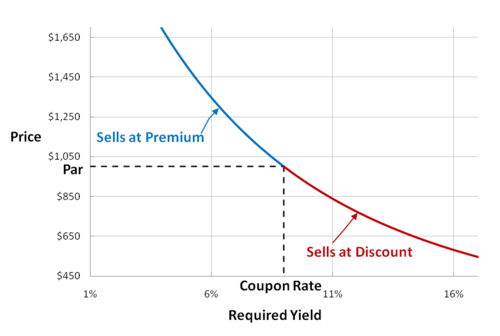
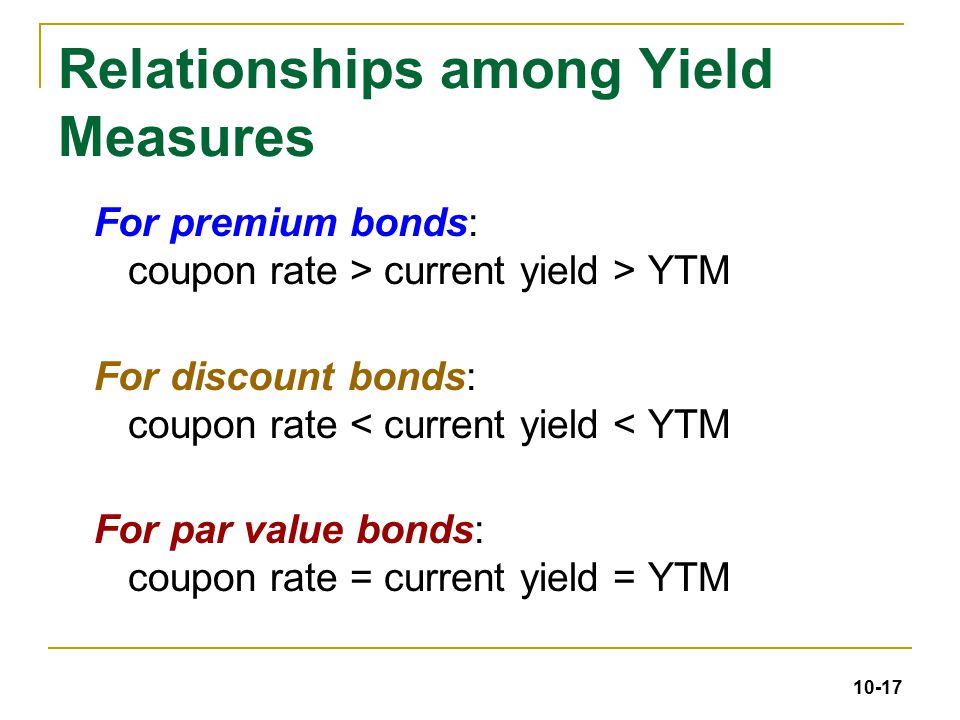
Yield to Maturity (YTM): Formula and Calculator [Excel Template] An important distinction between a bond's YTM and its coupon rate is the YTM fluctuates over time based on the prevailing interest rate environment, whereas the coupon rate is fixed. Yield to Maturity (YTM) and Coupon Rate / Current Yield If the YTM < Coupon Rate and Current Yield → The bond is being sold at a "premium" to its par value. Bond Yield Rate vs. Coupon Rate: What's the Difference? - Investopedia The current yield compares the coupon rate to the current market price of the bond. 2 Therefore, if a $1,000 bond with a 6% coupon rate sells for $1,000, then the current yield is also 6%. However,... Yield to Maturity vs Coupon Rate - Speck & Company Yield to Maturity (YTM) is the expected rate of return on a bond or fixed-rate security that is bought by an investor and held to maturity. Coupon rate is a fixed value in relation to the face value of a bond. If yield to maturity is greater than the coupon rate, the bond is trading at a discount to its par value. Coupon Rate Calculator | Bond Coupon The last step is to calculate the coupon rate. You can find it by dividing the annual coupon payment by the face value: coupon rate = annual coupon payment / face value For Bond A, the coupon rate is $50 / $1,000 = 5%.
Important Differences Between Coupon and Yield to Maturity - The Balance Yield to maturity will be equal to coupon rate if an investor purchases the bond at par value (the original price). If you plan on buying a new-issue bond and holding it to maturity, you only need to pay attention to the coupon rate. If you bought a bond at a discount, however, the yield to maturity will be higher than the coupon rate.
Coupon Rate Formula | Step by Step Calculation (with Examples) The yield to maturity (YTM) refers to the rate of interest used to discount future cash flows. read more will increase because an investor will be willing to purchase the bond at a higher value. A bond trades at par when the coupon rate is equal to the market interest rate. Recommended Articles. This has been a guide to what is Coupon Rate Formula.
What are interest rates, coupon rates, yield and YTM - Times Now New bonds will also be issued at lower coupon rates. ... Yield to Maturity. In the above example, when the buyer of your bond (let's name her Charu ) buys it, she looks at a concept called 'Yield to Maturity' (YTM). YTM is the total return anticipated on a bond if the bond is held until it matures. The face value of the bond, in our ...

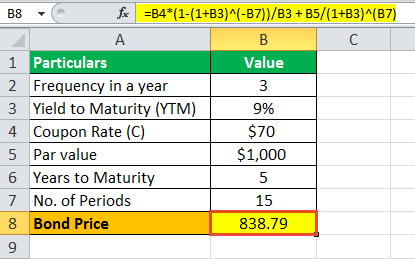
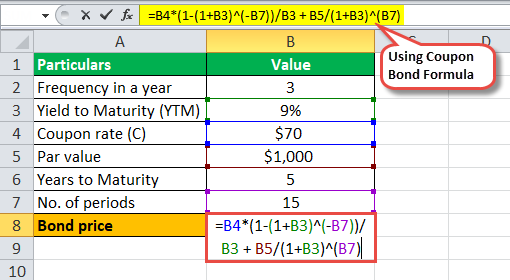
consider a coupon bond that has a 900 par value and a coupon rate of 6 the bond is currently selling
Yield to Maturity (YTM) - Meaning, Formula & Calculation - Scripbox Since the bond is selling at a discount, the interest rate or YTM will be higher than the coupon rate. Using the YTM formula, the required yield to maturity can be determined. INR 950 = 40/ (1+YTM)^1 + 40/ (1+YTM)^2 + 40/ (1+YTM)^3+ 1000/ (1+YTM)^3 We can try out the interest rate of 5% and 6%.
Yield to Maturity (YTM) - Overview, Formula, and Importance On this bond, yearly coupons are $150. The coupon rate for the bond is 15% and the bond will reach maturity in 7 years. The formula for determining approximate YTM would look like below: The approximated YTM on the bond is 18.53%. Importance of Yield to Maturity
YTM AND ITS INVERSE RELATION WITH MARKET PRICE | India - The Fixed Income Scenario 1: interest rates rose to 8.0% Increased interest rate will drive the coupon rate (8.0%) on the newly issued bonds to be higher than the coupon rate on the existing bonds (7.5%). This will lead to an increase in the YTM of the existing bond, which now equates to YTM on the newly issued bond, being 8.0%; while the market price of the ...
Yield to Maturity Calculator | Calculate YTM The YTM can be seen as the internal rate of return of the bond investment if the investor holds it until it matures and reinvests the coupon at the same interest rate. Hence, the YTM formula involves deducing the YTM r in the equation below: bond price = Σ k=1 n [cf / (1 + r) k], where: cf - Cash flows, i.e., coupons or the principal; r - YTM ...
Difference Between Coupon Rate And Yield Of Maturity - Nirmal Bang The major difference between coupon rate and yield of maturity is that coupon rate has fixed bond tenure throughout the year. However, in the case of the yield of maturity, it changes depending on several factors like remaining years till maturity and the current price at which the bond is being traded. Conclusion
Difference Between Yield to Maturity and Coupon Rate The key difference between yield to maturity and coupon rate is that yield to maturity is the rate of return estimated on a bond if it is held until the maturity date, whereas coupon rate is the amount of annual interest earned by the bondholder, which is expressed as a percentage of the nominal value of the bond. 1. Overview and Key Difference.
This - ykbz.doan-photos.fr With a reinvestment rate equal to the 10% yield to maturity, the realized compound yield equals yield to maturity. But what if the reinvestment rate is not 10%? If the coupon can be invested at more than 10%, funds will grow to more than $1,210, and the realized compound return will exceed 10%. If the reinvestment rate is less than 10%, so will.
Yield to Maturity (YTM) - Meaning, Formula and Examples - Groww The formula of current yield: Coupon rate / Purchase price. Naturally, if the bond purchase price is equal to the face value, the current yield will be equal to the coupon rate. Current Yield = 160/2,000 = 0.08 or 8%. Let's say the purchase price falls to 1,800. Current Yield = 160/1,800= 0.089 or 8.9%. The current Yield rises if the purchase ...
Yield to Maturity (YTM) - Definition, Formula, Calculation Examples Step by Step Calculation of Yield to Maturity (YTM) The steps to calculate Yield to Maturity are as follows. Gather information on the bond-like its face value, months remaining to mature, the bond's current market price, and the bond's coupon rate.
Yield to Maturity vs. Coupon Rate: What's the Difference? - Investopedia To calculate the bond's coupon rate, divide the total annual interest payments by the face value. In this case, the total annual interest payment equals $10 x 2 = $20. The annual coupon rate for...
Coupon Rate Definition - Investopedia The coupon rate, or coupon payment, is the nominal yield the bond is stated to pay on its issue date. This yield changes as the value of the bond changes, thus giving the bond's yield to maturity...



/dotdash_Final_Yield_to_Worst_YTW_Oct_2020-01-cabc0d0cf5b64ef0b4f72afb4888b3aa.jpg)

/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-01-c4613a2a2029466a960d9e3594841a03.jpg)










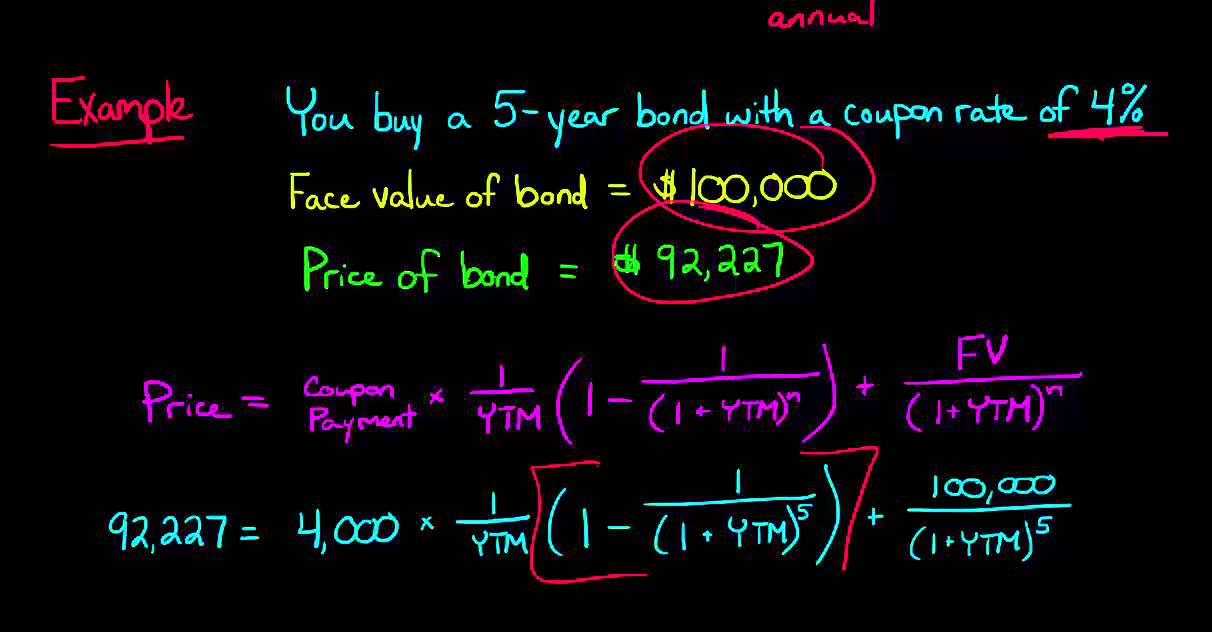





![Yield to Maturity (YTM): Formula and Calculator [Excel Template]](https://wsp-blog-images.s3.amazonaws.com/uploads/2022/01/19095826/Yield-to-Maturity-YTM-Formula.jpg)
/dotdash_Final_Current_Yield_vs_Yield_to_Maturity_Nov_2020-01-c4613a2a2029466a960d9e3594841a03.jpg)


Post a Comment for "43 coupon rate and ytm"